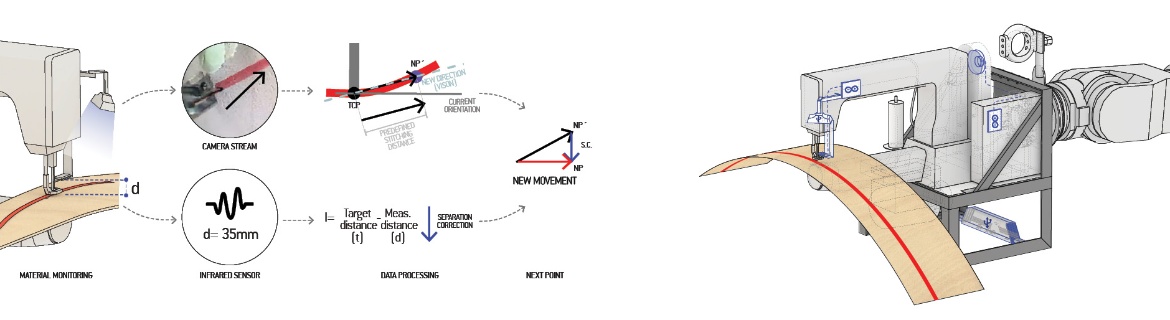
The course introduces a new methodology for digital design and fabrication; contrary to traditional notions of design, behavioural strategies for fabrication are not based on the execution of a priori defined abstract plans, such as detailed digital design models, but are based on the concept of execution of tasks. Tasks represent design intention and unfold in a nondeterministic way based on the constant interaction of the machine/robot/agent with the material and its environment through sensor-actuator feedback.
The course introduces students to the topic of behavioural fabrication and related computational techniques including: (i) Agent-based and behavioural models, (ii) Sensor feedback and machine vision, (iii) Online robotic control methods, (iv) Methods for environmental analysis and mapping.
At the core of the research lie the analysis, abstraction, translation and implementation of fabrication-oriented behaviours for the production of physical prototypes.
Students are expected a high degree of proficiency in computer programming (either in C# or in python), and are also are expected to be familiar with industrial robotics from the previous seminar courses offered by ICD in computation and robotic fabrication.
Brooks, Rodney A. 1990. Elephants Don’t Play Chess. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 6 (1-2): 3–15.
Dörfler K, Rist F, Rust R. 2012. Interlacing: an experimental approach to integrating digital and physical design methods. In Rob|Arch 2012: Robotic fabrication in architecture, art and industrial design. Springer, Vienna, 2013, pp. 82–91.
Johns, Ryan Luke, Axel Kilian, and Nicholas Foley. 2014. Design Approaches Through Augmented Materiality and Embodied Computation. In Robotic Fabrication in Architecture, Art and Design 2014, edited by Wes McGee and Monica Ponce de Leon, 319–332. Springer International Publishing.
Menges, A., 2008. Integral formation and materialisation: Computational form and material gestalt. In K. R. Klinger & B. Kolarevic (Eds.), Manufacturing Material Effects: Rethinking Design and Making in Architecture, pp. 195–210. New York: Routledge.

